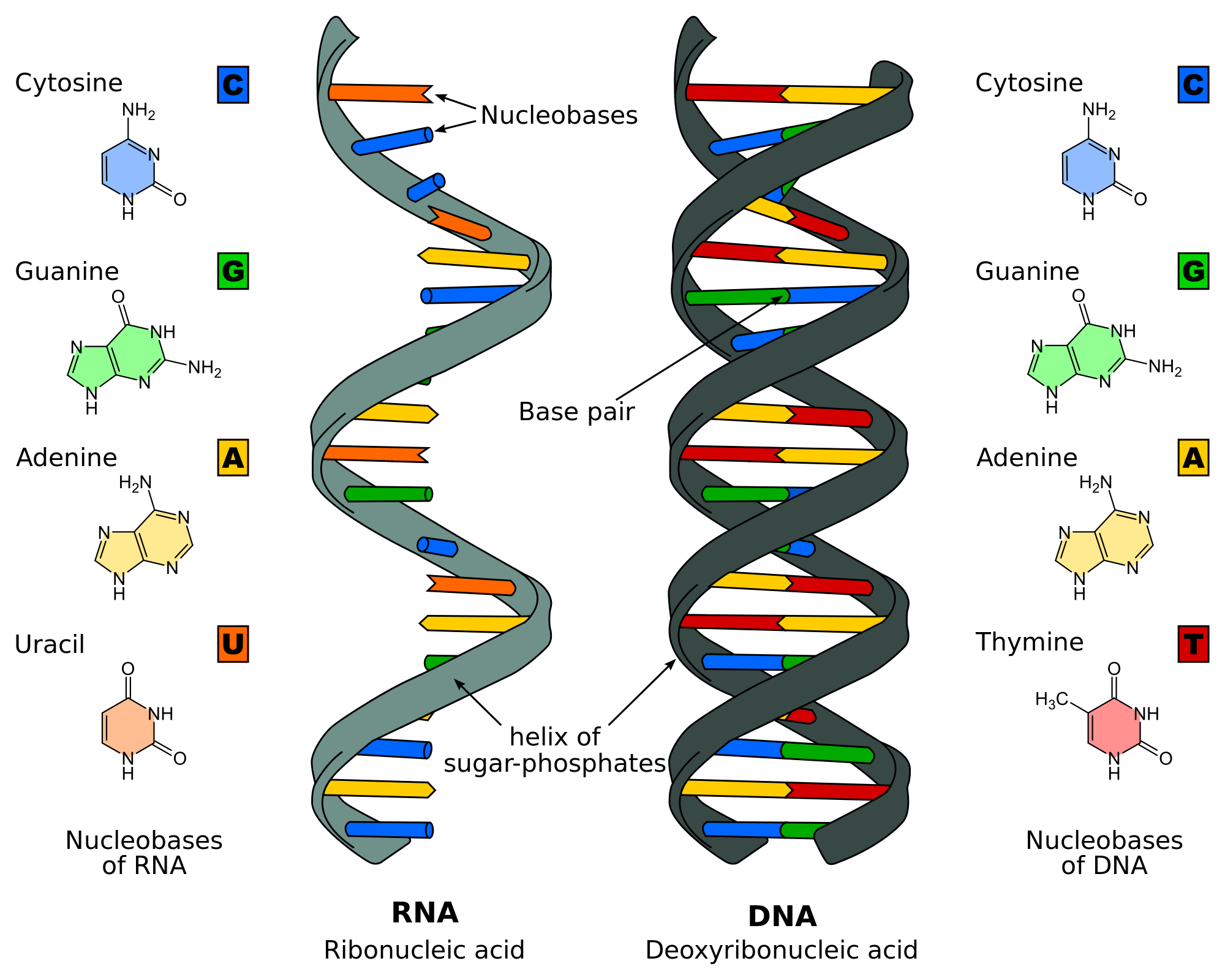
For this section, I had to look into my notes, but only to see how to spell some words so that doesn't count! Protein synthesis is how proteins are created from DNA. RNA polymerase makes a copy of the DNA, which is deoxyribose nucleic acid. DNA is made from a sugar, the deoxyribose, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base, which can be either Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, or Cytosine. DNA has two strands, and twists into a double helix shape, with bases matching together. The bases match with each other, Cytosine with Guanine, and Adenine with Thymine. The copy is called RNA, which is very similar, except Thymine is replaced with Uracil, and it is single stranded instead of double stranded. This is messenger RNA. It goes out of the nucleus and to a ribosome, where it is read. Each codon, which is 3 bases, codes for one amino acid. An amino acid can be coded for by several different codons. Transfer RNA brings the amino acid to the ribosome to build the protein, and matching base pairs for the messenger RNA.
Mutations are changes in DNA. They can be deadly, or do nothing at all, which is called a silent mutation. One type of mutation is a point mutation, where a single base pair is changed. One type of point mutation is a substitution, where one base pair is substituted for another one. This type of mutation causes little to no damage, because some amino acids can be coded for in several ways, and if it does change the amino acid, it only changes one of them, which will have a small effect. The other type of point mutation is a frameshift mutation, where one base pair is added or removed. This has a large effect, and can completely ruin a protein because in addition to changing the current codon, it shifts over all following codons, which can cause a completely different protein to be made, or cause no protein to be made at all. There are other mutations that aren't point mutations, such as inversions, which cause a piece of DNA to become unattached, and reattach backwards. Translocations are when DNA from one chromosomes attaches to a different chromosome. Mutations are caused by mutagens, such as UV, (checks notes for other mutagens) nuclear radiation, X-rays, and toxins(closes notebook).
 |
| Example of a mutation. |
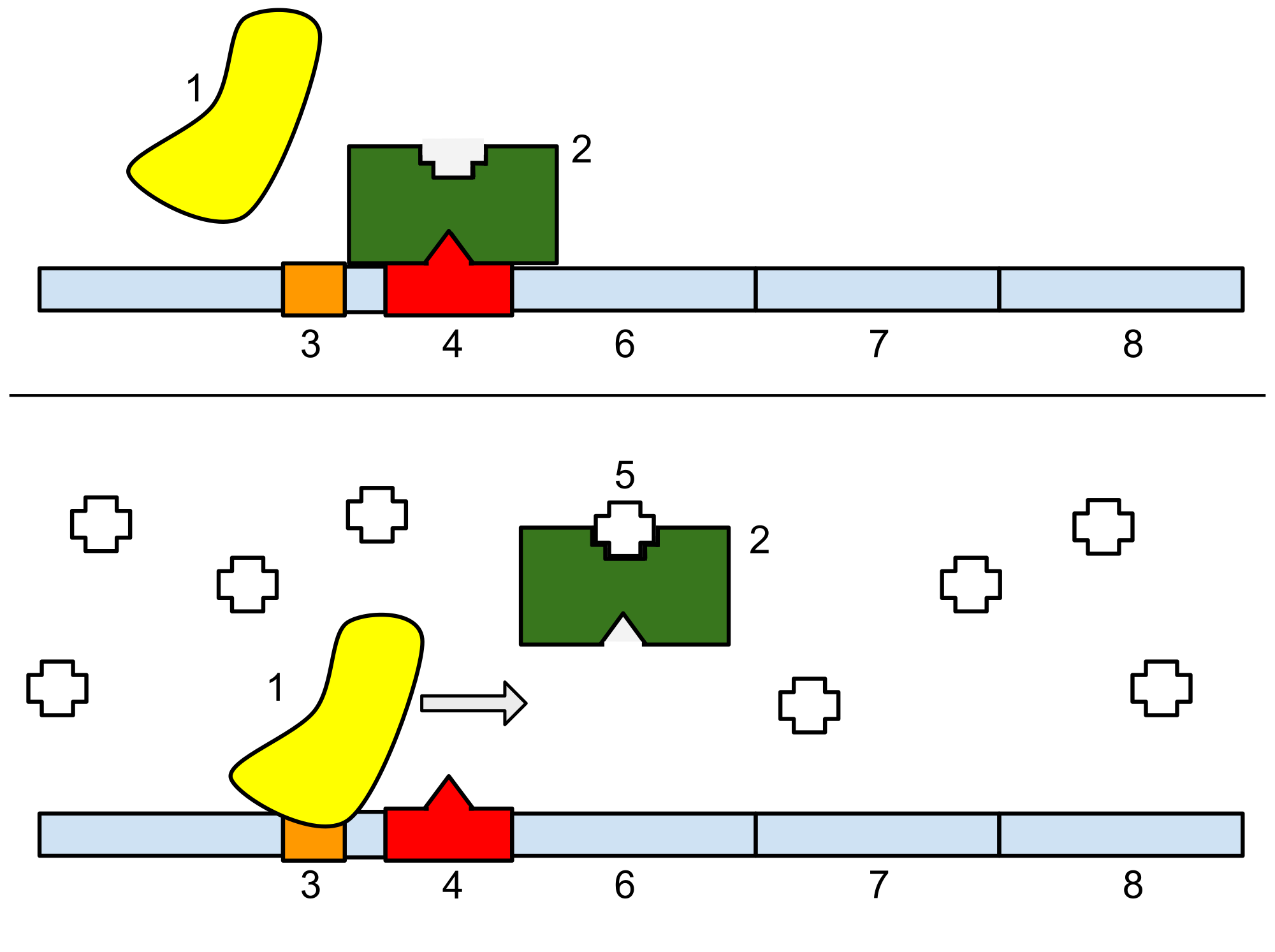 |
| 1: RNA polymerase. 2: Repressor. 3: Operator. 4: Promoter. 5: Lactose |
No comments:
Post a Comment